A star is a hot, glowing ball of gas. When you look up in the night sky, you can see countless twinkling stars. Can you see any stars during the daytime? Of course! The light of daytime comes from our closest star: the Sun.
All 3D models in the page have loaded
Explore the Sun! Click and drag to rotate the Sun. Scroll or pinch to zoom in and out. Credit: NASA Visualization Technology Applications and Development (VTAD)
Just how close is the Sun to Earth? Way, way closer than other stars, but still pretty far away. It’s approximately 93 million miles away from Earth. That’s 400 times farther than the distance between Earth and the Moon!
However, it’s a good thing that Earth isn’t too close to the Sun. If we were too close, it would be way too hot to live here. The Sun’s surface is very hot, and its atmosphere is even hotter. And the Sun’s core is the hottest part of all, at a sizzling 27 million degrees Fahrenheit!
Our Sun is about 100 times wider than Earth, but it is just an average sized star. Astronomers have found some stars that are 100 times bigger than the Sun and others that are 10 times smaller.
The Sun is also right in the middle of its lifecycle. Right now, our Sun is in a stage called yellow dwarf. It is about 4.5 billion years old. In another 5 billion years the Sun will become a big, cool star called a red giant. A few billion years after that, it will become a small white dwarf star. It will shrink to around the same size as Earth, but it will weigh 20,000 times more.
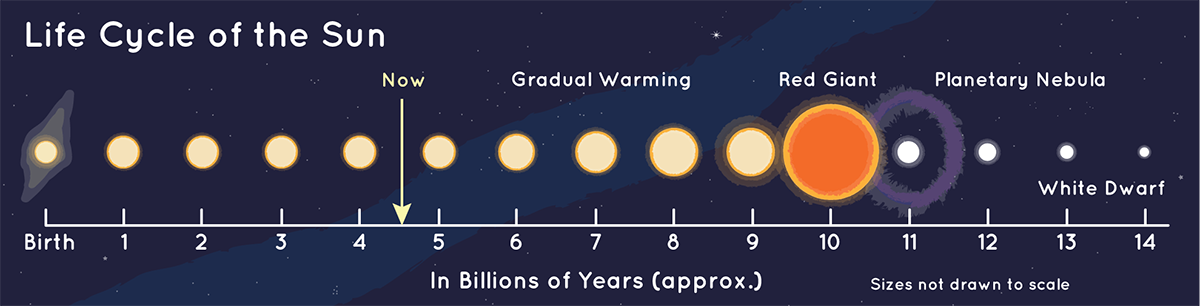
Click the above image to expand it. Our Sun is in the middle of its lifecycle. It is a yellow dwarf star. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
But even though our Sun is kind of an ordinary star, there are also a few things that make our Sun quite special. For example…
We can’t live without the Sun!
Life on Earth depends on the Sun. Here are just a few reasons why:
- The Sun’s gravity holds our entire solar system together. Our solar system is even named after the Sun (the Latin word for Sun is “sol”).
- Heat from the Sun makes Earth warm enough to live on.
- Without light from the Sun, there would be no plants or animals—and, therefore, no food and we wouldn’t exist.
Heat and light might be important for life on Earth, but the Sun sends other stuff, too. The Sun sends lots of other energy and small particles toward Earth. Earth’s protective magnetic field and atmosphere shields us from most of the energy and particles. But sometimes a big stream of these particles reaches Earth and interacts with the gases at the outer edge of our atmosphere. This causes streams of light in the sky, called auroras.
Where does the Sun's energy come from?
The Sun's heat influences the environments of all the planets, dwarf planets, moons, asteroids, and comets in our solar system. How does a big ball of hydrogen create all that heat? Learn all about it in this video!
(taken from:https://spaceplace.nasa.gov/all-about-the-sun/en/)


.jpg)
.png)









.png)
.png)